Medical term:
Ca
diltiazem hydrochloride
Pharmacologic class: Calcium channel blocker
Therapeutic class: Antianginal, antiarrhythmic (class IV), antihypertensive
Pregnancy risk category C
Action
Inhibits calcium from entering myocardial and vascular smooth-muscle cells, thereby depressing myocardial and smooth-muscle contraction and decreasing impulse formation and conduction velocity. As a result, systolic and diastolic pressures decrease.
Availability
Capsules (extended-release, sustained-release): 60 mg, 90 mg, 120 mg, 180 mg, 240 mg, 300 mg, 360 mg, 420 mg
Injection: 5 mg/ml in 10-ml vials, 100-mg Monovial
Tablets: 30 mg, 60 mg, 90 mg, 120 mg
Indications and dosages
➣ Angina pectoris and vasospastic (Prinzmetal's) angina; hypertension; supraventricular tachyarrhythmias; atrial flutter or fibrillation
Adults: 30 to 90 mg P.O. three to four times daily (tablets), or 60 to 120 mg P.O. b.i.d. (sustained-release), or 180 to 240 mg P.O. once daily (extended-release), adjusted after 14 days as needed, up to a total daily dosage of 360 mg. Or 0.25 mg/kg by I.V. bolus over 2 minutes; if response is inadequate after 15 minutes, may give 0.35 mg/kg over 2 minutes; may follow with continuous I.V. infusion at 10 mg/hour (at a range of 5 to 15 mg/hour) for up to 24 hours.
Dosage adjustment
• Severe hepatic or renal impairment
• Elderly patients
Off-label uses
• Unstable angina, coronary artery bypass graft surgery
• Tardive dyskinesia
• Migraine
• Hyperthyroidism
• Raynaud's phenomenon
Contraindications
• Hypersensitivity to drug
• Atrial flutter or fibrillation associated with shortened refractory period (Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome, with I.V. use)
• Recent myocardial infarction or pulmonary congestion
• Cardiogenic shock, concurrent I.V. beta-blocker therapy, ventricular tachycardia, neonates (with I.V. use, because of benzyl alcohol in syringe formulation)
• Sick sinus syndrome, second- or third-degree atrioventricular block (except in patients with ventricular pacemakers)
• Hypotension (systolic pressure below 90 mm Hg)
Precautions
Use cautiously in:
• severe hepatic or renal impairment, heart failure
• history of serious ventricular arrhythmias
• concurrent use of I.V. diltiazem and I.V. beta blockers
• elderly patients
• pregnant or breastfeeding patients
• children (safety not established).
Administration
• When giving I.V., dilute in dextrose 5% in water or normal saline solution.
• Give I.V. bolus dose over 2 minutes; a second bolus may be given after 15 minutes.
• Administer continuous I.V. infusion at a rate of 5 to 15 mg/hour.
☞ When giving by continuous I.V. infusion, make sure emergency equipment is available and that patient has continuous ECG monitoring with frequent blood pressure monitoring.
• Don't crush tablets or sustained-release capsules; they must be swallowed whole.
• Withhold dose if systolic blood pressure falls below 90 mm Hg, diastolic pressure is below 60 mm Hg, or apical pulse is slower than 60 beats/minute.
Adverse reactions
CNS: headache, abnormal dreams, anxiety, confusion, dizziness, drowsiness, nervousness, psychiatric disturbances, asthenia, paresthesia, syncope, tremor
CV: peripheral edema, bradycardia, chest pain, hypotension, palpitations, tachycardia, arrhythmias, heart failure
EENT: blurred vision, tinnitus, epistaxis
GI: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation, dyspepsia, dry mouth
GU: urinary frequency, dysuria, nocturia, polyuria, gynecomastia, sexual dysfunction
Hematologic: anemia, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia
Metabolic: hyperglycemia
Musculoskeletal: joint stiffness, muscle cramps
Respiratory: cough, dyspnea
Skin: rash, dermatitis, flushing, diaphoresis, photosensitivity, pruritus, urticaria, erythema multiforme
Other: unpleasant taste, gingival hyperplasia, weight gain, decreased appetite, Stevens-Johnson syndrome
Interactions
Drug-drug. Beta-adrenergic blockers, digoxin, disopyramide, phenytoin: bradycardia, conduction defects, heart failure
Carbamazepine, cyclosporine, quinidine: decreased diltiazem metabolism, increased risk of toxicity
Cimetidine, ranitidine: increased blood level and effects of diltiazem
Fentanyl, nitrates, other antihypertensives, quinidine: additive hypotension
HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors, imipramine, sirolimus, tacrolimus: increased blood levels of these drugs
Lithium: decreased lithium blood level, reduced antimanic control
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: decreased antihypertensive effect of diltiazem
Theophylline: increased theophylline effects
Drug-diagnostic tests. Hepatic enzymes: increased levels
Drug-food. Grapefruit juice: increased blood level and effects of diltiazem
Drug-behaviors. Acute alcohol ingestion: additive hypotension
Patient monitoring
• Check blood pressure and ECG before starting therapy, and monitor closely during dosage adjustment period. Withhold dose if systolic pressure is below 90 mm Hg.
☞ Monitor for signs and symptoms of heart failure and worsening arrhythmias.
• Supervise patient during ambulation.
Patient teaching
• Instruct patient to swallow extended-release capsules whole and not to crush or chew them.
• Advise patient to change position slowly to minimize light-headedness and dizziness.
• Caution patient to avoid driving and other hazardous activities until he knows how drug affects concentration and alertness.
• As appropriate, review all other significant and life-threatening adverse reactions and interactions, especially those related to the drugs, tests, foods, and behaviors mentioned above.
Cardizem
(kär′dĭ-zĕm′)Cardizem®
Diltiazem, see there.doxazosin mesylate
Pharmacologic class: Sympatholytic, peripherally acting antiadrenergic
Therapeutic class: Antihypertensive
Pregnancy risk category C
Action
Blocks alpha1-adrenergic receptors, promoting vasodilation. Also reduces urethral resistance, relieving obstruction and improving urine flow and other symptoms of benign prostatic hypertrophy (BPH).
Availability
Tablets: 1 mg, 2 mg, 4 mg, 8 mg
Tablets (extended-release): 4 mg, 8 mg
Indications and dosages
➣ Hypertension
Adults: 1 mg P.O. once daily. May increase dosage gradually q 2 weeks, up to 2 to 16 mg daily, as needed.
➣ BPH
Adults: 1 mg P.O. once daily. May increase dosage gradually, up to 8 mg daily, as needed. Or, initially 4 mg (extended-release) P.O. daily. May increase dosage to 8 mg daily, as needed, at 3- to 4-week intervals.
Off-label uses
• Pheochromocytoma
• Syndrome X
Contraindications
• Hypersensitivity to drug, its components, or quinazoline derivatives
Precautions
Use cautiously in:
• renal or mild or moderate hepatic impairment, coronary insufficiency, or preexisting severe GI narrowing
• severe hepatic impairment (extended-release form not recommended)
• intraoperative floppy iris syndrome
• concurrent use of strong CYP3A4 inhibitor (such as atazanavir, clarithromycin, indinavir, itraconazole, ketoconazole, nefazodone, nelfinavir, ritonavir, saquinavir, telithromycin, or voriconazole), phosphodiesterase-5 (PDE-5) inhibitors
• elderly patients
• pregnant or breastfeeding patients (extended-release form not recommended in breastfeeding patients)
• children (safety not established).
Administration
• Give initial immediate-release dose at bedtime to minimize orthostatic hypotension and syncope.
• Give initial extended-release dose at breakfast.
• Be aware that extended-release tablets aren't indicated for hypertension.
• Be aware that prostate carcinoma should be ruled out before giving drug for BPH.
• Know that incidence of orthostatic hypotension increases greatly when daily dosage exceeds 4 mg and that it usually occurs within 6 hours of administration.
☞ If new or worsening signs or symptoms of angina pectoris occur, discontinue drug.

Adverse reactions
CNS: dizziness, vertigo, headache, depression, drowsiness, fatigue, nervousness, weakness, asthenia
CV: orthostatic hypotension, chest pain, palpitations, tachycardia, arrhythmias
EENT: abnormal or blurred vision, conjunctivitis, epistaxis, rhinitis, pharyngitis
GI: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation, abdominal discomfort, flatulence, dry mouth
GU: decreased libido, sexual dysfunction
Respiratory: dyspnea
Musculoskeletal: joint pain, arthritis, gout, myalgia
Skin: flushing, rash, pruritus
Other: edema
Interactions
Drug-drug. Clonidine, nitrates, other antihypertensives: decreased antihypertensive effect
Drugs that reduce GI motility leading to markedly prolonged GI retention times (such as anticholinergics): increased systemic exposure to doxazosin
PDE-5 inhibitors: increased risk of symptomatic hypotension
Drug-diagnostic tests. Neutrophils, white blood cells: decreased counts
Drug-food. Any food: increased drug plasma Cmax (extended-release form)
Patient monitoring
• Monitor blood pressure with patient lying down and standing up every 2 to 6 hours after initial dose or after a dosage increase (when orthostatic hypotension is most likely to occur).
Patient teaching
• Tell patient to swallow extended-release tablets whole and not to chew, divide, cut, or crush them.
• Caution patient not to drive or perform other activities requiring alertness for 12 to 24 hours after first dose.
• Tell patient to move slowly when sitting up or standing, to avoid dizziness or light-headedness from sudden blood pressure decrease.
• Advise patient to report episodes of dizziness or palpitations.
• As appropriate, review all other significant and life-threatening adverse reactions and interactions, especially those related to the drugs and tests mentioned above.
doxazosin
(dox-ay-zoe-sin) ,Cardura
(trade name),Cardura XL
(trade name)Classification
Therapeutic: antihypertensivesPharmacologic: peripherally acting antiadrenergics
Indications
Action
Therapeutic effects
Pharmacokinetics
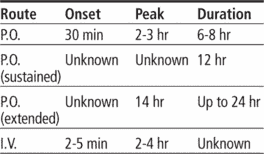
Time/action profile
| ROUTE | ONSET | PEAK | DURATION |
|---|---|---|---|
| PO† | 1–2 hr | 2–6 hr | 24 hr |
| PO-XL‡ | 5 wk | unknown | unknown |
Contraindications/Precautions
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Central nervous system
- dizziness (most frequent)
- headache (most frequent)
- depression
- drowsiness
- fatigue
- nervousness
- weakness
Ear, Eye, Nose, Throat
- abnormal vision
- blurred vision
- conjunctivitis
- epistaxis
- intraoperative floppy iris syndrome
Respiratory
- dyspnea
Cardiovascular
- first-dose orthostatic hypotension (most frequent)
- arrhythmias
- chest pain
- edema
- palpitations
Gastrointestinal
- abdominal discomfort
- constipation
- diarrhea
- dry mouth
- flatulence
- nausea
- vomiting
Genitourinary
- ↓ libido
- priapism
- sexual dysfunction
Dermatologic
- flushing
- rash
- urticaria
Musculoskeletal
- arthralgia
- arthritis
- gout
- myalgia
Interactions
Drug-Drug interaction
↑ risk of hypotension with sildenafil, tadalafil, vardenafil, other antihypertensives, nitrates, or acute ingestion of alcohol.NSAIDs, sympathomimetics, or estrogens may ↓ effects of antihypertensive therapy.Route/Dosage
HypertensionAvailability (generic available)
Nursing implications
Nursing assessment
- Monitor BP and pulse 2–6 hr after first dose, with each increase in dose, and periodically during therapy. Report significant changes.
- Assess for first-dose orthostatic hypotension and syncope. Incidence may be dose related. Observe patient closely during this period and take precautions to prevent injury.
- Monitor intake and output ratios and daily weight, and assess for edema daily, especially at beginning of therapy. Report weight gain or edema.
- BPH: Assess patient for symptoms of prostatic hyperplasia (urinary hesitancy, feeling of incomplete bladder emptying, interruption of urinary stream, impairment of size and force of urinary stream, terminal urinary dribbling, straining to start flow, dysuria, urgency) prior to and periodically during therapy.
Potential Nursing Diagnoses
Impaired urinary elimination (Indications)Risk for injury (Side Effects)
Implementation
- Do not confuse Cardura with Coumadin.
- Oral: Administer daily dose at bedtime.
- XL tablets should be swallowed whole; do not break, crush, or chew.
- Hypertension: May be administered concurrently with a diuretic or other antihypertensive.
Patient/Family Teaching
- Emphasize the importance of continuing to take this medication, even if feeling well. Instruct patient to take medication at the same time each day. Take missed doses as soon as remembered unless almost time for next dose. Do not double doses.
- May cause drowsiness or dizziness. Advise patient to avoid driving or other activities requiring alertness until response to medication is known.
- Caution patient to change positions slowly to decrease orthostatic hypotension. May cause syncopal episodes, especially within first 24 hr of therapy, with dose increase, and with resumption of therapy after interruption.
- Instruct patient to notify health care professional of all Rx or OTC medications, vitamins, or herbal products being taken and to avoid concurrent use of alcohol or OTC medications and herbal products, especially cold preparations, without consulting health care professional, especially cough, cold, or allergy remedies.
- Advise male patient to notify health care professional if priapism or erection of longer than 4 hr occurs; may lead to permanent impotence if not treated.
- Advise female patient to notify health care professional if pregnancy is planned or suspected or if breast feeding.
- Emphasize the importance of follow-up visits to determine effectiveness of therapy.
- Hypertension: Instruct patient and family on proper technique for BP monitoring. Advise them to check BP at least weekly and report significant changes.
- Encourage patient to comply with additional interventions for hypertension (weight reduction, low-sodium diet, smoking cessation, moderation of alcohol consumption, regular exercise, and stress management).
Evaluation/Desired Outcomes
- Decrease in BP without appearance of side effects.
- Decrease in urinary symptoms of BPH.
Cardura
(kär-do͝or′ə)Cardura®
Doxazosin mesylate, see there.Latest Searches:
zygomaticofrontal - zygomaticofacialis - zygomaticofacial - zygomaticoauricular - zygomatico - zygomatici - zygomatica - zygomatic - zygoma - zygomas - zygodactyly - Zygocotyle - zygion - zygia - zygapophysis - zygapophysiales - zygapophysial - zygapophyseales - zygapophyseal - zygal -
- Service manuals - MBI Corp